Productivity and Content of Pharmaceutical Indices of Sedum aizoon l. At Different Ratios of N, P, K-Juniper Publishers
Journal of Agriculture Research- Juniper Publishers
In the experiments of mineral nutrition optimization
of valuable herb Sedium aizoon L. grown in open air hydroponic
conditions it was revealed the significant influence of N, P, K ratio in
nutrient solution on productivity and content of
physiological-biochemical, pharmaceutical indices of plant. Moreover,
the optimum ratio of N, P, K was 10:40:50 atom% for the output of
medicinal raw material, and in the roots it was 16:23:61; 17:22:61;
15:25:60; 21:21:58; 15:43:42 և 26:18:56 atom% for biologically active
compounds saponins, arbutin, β-sitosterol, olienic acid, tannins and
еxtractives, accordingly.
Keywords: Nutrition optimalization; Hydroponics; Sedium aizoon L., Physiological-pharmacological indices; Productivity
Introduction
Medicinal herb Sedum aizoon L. have been introduced
to soilless culture taking into consideration the unique properties and
high demand of stimulating and adaptive plant species. Long-term
researches approved high productivity and possibility of hydroponic
cultivation of Sedum aizoon L. and revealed its agro-radiochemical,
physiological–biochemical characteristics in conditions of hydroponics
and soil culture [1-4]. At the same time, in the Institute of
Hydroponics Problems of NAS RA scientific experiments were done for
optimization of the mineral nutrition of some medicinal, essential oil
bearing, dye-bearing crops, also mathematical models of plant
productivity increase have been received, and the influence of N, P, K
ratio of the nutrient solution on productivity of plants and on
stimulation of bioactive compounds’ biosynthesis has been confirmed
[5-8].
The aim of research was to study the influence of N,
P, K different ratios on the plant productivity taking account above
mentioned and medicinal specificities and prospects of Sedum aizoon L.
Materials and Methods
Sedum aizoon L. is a perennial herb with 25-45cm
height that belongs to the Grassulaceae family. The root and over ground
parts of the plant are used for medical purposes. In the roots of plant
there were found carbohydrates, oleic acid, β-sitosterol, phenols and
their derivatives (arbutin), tannins, triterpenoid saponins that have
stimulating properties. In the leaves of plant there were found vitamin
C, carotenoids, tannins and negligible amounts of
arbutin and saponins. The plant is used for treatment of pneumo
nia, hepatitis, kidney dieseases and other diseases. It has also
abilities to reduce temperature, heal wounds and raise vitality [9-11].
The experiments were done with the 8 repeats in
hydroponic vegetative vessels with 0.16m2 surface, where the mixture of
volcanic slag and gravel with 1:1 ratio was used as a substrate. Plants
were nourished two times during a day with the Davtyan’s 1N nutrient
solution [12] with the following three proportions of N, P, K:
N70P15K15, N15P70K15 and N15P15K70 atom %. The methods of Homes’s
Systematic variations [13] and Vakhmistrov’s “correlation probing” [14]
were used to clarify the optimal ratio of N, P, K, and to count
correlation coefficient between plant productivity and N, P, K ratio in
nutrient solution. Physiological-biochemical and medicinal analyses of
experimental plants were done during vegetation: water-holding forces,
the sap osmotic pressure in the leaves were measured according Gusev
[15], the content of photosynthetic pigments was estimated according
Wettstein [16], the content of vitamin C was determined according
Yermakov [17] and the content of tannins, extractive compounds and
humidity in the dry medicinal raw material was defined according SPh XI
[18]. The amount of saponins, arbutin, β-sytosterin, oleic acid in the
roots was determined by the method of preparative thin layer
chromatography. The samples of “Sigma Aldrich” firm were used as
standards.
Results and Discussion
The experiment results for optimization of Sedum
aizoon L. mineral nutrition is shown in the Tables 1-4. It was found
that high amount of potassium in the nutrient solution promotes the
increase of plant productivity and improvement of some medicinal
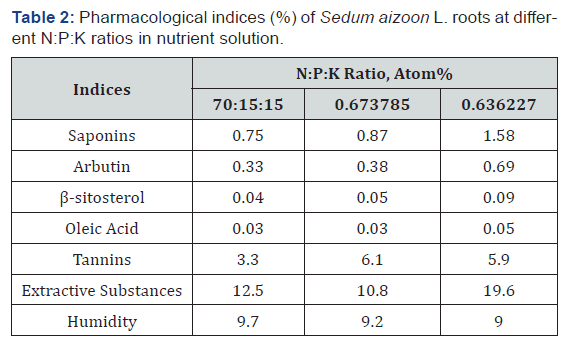
indices (Table 1,2).
The content of bioactive substances in the variant with highest
content of K exceeded the variant with highest content of N,
in average, 1.6-2.3 times and the variant with highest content of
P 1.7-1.8 times. The high amount of nitrogen in nutrient solution
had a negative influence on tannins content in the roots and accumulation
of dry medicinal raw material.

N, P, K effective ratios were calculated theoretically for dry
medicinal raw material of Sedum aizoon L. using the method of
“systematic variations” of Homes: 10:40: 50 atom % for output of
over ground mass and total medicinal raw material and 11:40:49
atom % for roots. Also, correlation coefficients between the plant
productivity and N:P:K ratio in the nutrient solution was defined
that were-0.998; -0.999 and -0.997, respectively.
Mathematical models of plant productivity enhancement were
developed in form of regression equations (for over ground mass:
y=19.82-0.27x; for roots: y=11.79-0.157x; for total medicinal
raw material: y=30.17-0.383x). The analyses of equations allow
to suppose that it is possible to receive maximum harvest of Sedum
aizoon L. at nutrient solution with optimal N:P:K ratio: for
over ground mass it equals to 19.82g/plant, for roots it is 11.79 g/
plant, for total medicinal raw material it makes up 30.17g/plant
and the 1 atom % shift from above mentioned values will bring to
the decrease of yield on 0.270g/plant; 0.157g/plant; 0.383g/plant
amount, respectively.
Similar calculations were done also for the definition of bioactive
compounds (saponins, arbutin, β-sitosterol, oleic acid, tannins
and extractive substances) content in the roots of Sedum aizoon L.
(Table 3).

Mathematical models of plant productivity enhancement were
brought out in form of regression equations for the content of:
a. Saponins: y=1.74-0.0185x.
b. Arbutin: y=0.77-0.0081x.
c. β-sitosterol: y=0.1-0.0011x.
d. Oleic acid: y=0.057-0.00054x.
e. Tannins: y=8.7-0.0983x.
f. Extractive substances: y=22.84-0.223x.
These equations prove, that in optimal conditions of nutrient
solution it is possible to receive maximum amount of saponins, arbutin,
β-sitosterol, oleic acid, tannins and extractive substances in
the roots of Sedum aizoon L.
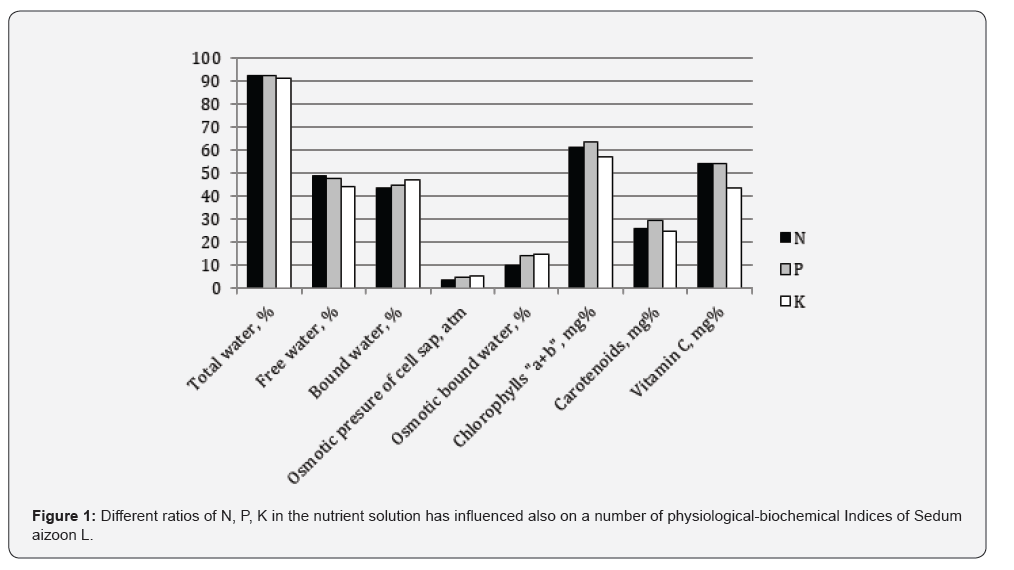
Thus, relatively high accumulation of water’s more mobile
fraction, chlorophyll (a+b) and vitamin C was observed in case
of nitrogen and phosphorus high portions in nutrient solution,
and an increase of sap osmotic pressure and osmotic bound water
was recorded in variants with predominance of phosphorus
and potassium. Relatively high portion of phosphorus in nutrient
solution provided the increase of carotenoids content in the leaves
(Figure).
Conclusion
The ratio of N, P, K in Davtyan’s 1N nutrient solution sufficiently
influences on the productivity and bioactive substances
content of Sedum aizoon L. Whereupon, effective ratios of N, P, K
are 10:40:50 atom% in the case of total medicinal raw material
output, and are 16:23:61; 17:22:61; 15:25:60; 21:21:58; 15:43:42
and 26:18:56 atom % in the roots in the case of bioactive compounds
saponins, arbutin, β-sitosterol, oleic acid, tannins and extractive
substances, respectively.
To know more about Journal of Agriculture Research- https://juniperpublishers.com/artoaj/index.php
To know more about open access journal publishers click on Juniper publishers



Comments
Post a Comment