Effect of the Extract of Balloon Pepper (Capsicum Baccatum var. Pendulum) on Lipid Peroxidation and Microbiology of Pork Sausage-Juniper Publishers
Journal of Agriculture Research- Juniper Publishers
The reduction of the quality of foods usually associates with the deterioration of their compounds. Lipid oxidation is the main reason for this deterioration [1]. The phospholipids, polyunsaturated fatty acid together with the oxygen, heme pigments, and some metallic ions influence the deterioration process of processed foods either directly, or indirectly [2]. Oxidation processes affect the nutritional, sensorial values of the products, and the level of Thiobarbituric Acid Reacting Substances (TBARS), which is the main parameter to assess the lipid oxidation [3]. Brazilian legislation provides limits to the use of synthetic antioxidants, and, even the efficiency in food preservation, several studies demonstrate their risks for human health [4]. The carcinogenic potential associated with the use of synthetic antioxidants and other potential damages to health increased the interest in the use of natural antioxidants [5]. In this context, studies involving the effect of time and storage conditions of meat products are essential factors in meat processing, since problems related to storage stability are common [6]. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the influence of the use of natural antioxidants based on extracts of the balloon pepper (Capsicum baccatum var. pendulum) on the oxidation of fresh pork sausage and smoked and on the microbiology of fresh pork sausage.
Materials and Methods
The extraction method was adapted from [7], choosing for the production of oleoresins. In the beginning, the fruits were cut to extract the seeds and washed with tap water, weighed, and placed on an air-circulation oven at 40ºC, until reaching a constant mass. The ethanol was the solvent used for the preparation of the extraction. After the drying, fruits were minced and submitted to extraction in the Soxhlet equipment, using ethanol 70% (Fruitsolvent ratio: 1:10 weight/volume) for four hours. The extracts were evaporated by a rotary evaporator at 79ºC. After this process, the antioxidant extract of the balloon pepper was obtained. Five different formulations of fresh pork sausage and smoked sausage were produced, for the exclusive study of lipid oxidation: Positive control, F1 (negative control), F2 (0.5%), F3 (1%), and F4 (1.5% of antioxidant extract of the balloon pepper). The formulations were produced promoting the substitution of the synthetic antioxidant with the natural one. A positive control using sodium erythorbate, and a negative control without any antioxidant product were included in the experiment. After their production, the sausages were vacuum-sealed and stored at -18ºC for further analyses of lipid oxidation. Microbiological analysis of the samples was performed and results were compared with the standards recommended in the RDC 12 [8], for coliforms at 45ºC (Most Probable Number method), Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus (Presence or absence), and Salmonella spp. (presence or absence). The results were submitted to Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) at 5% probability. The treatments were compared by the test Student- Newman-Keuls (SAS, 2009 version 9.3).
Results and Discussion
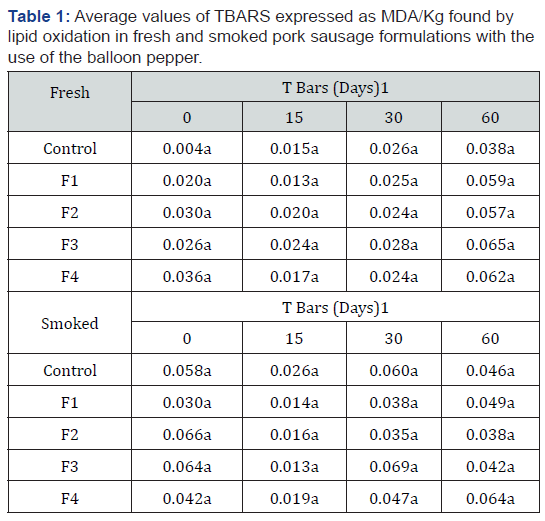
The natural antioxidant (the extract of balloon pepper) was added at different concentrations in the different formulations in order to delay lipid oxidation and extend the shelf life of the fresh sausage. Table 1 present the values of TBARS obtained Table 2. We did not find significant differences (P>0.05) among the treatments, and at different times of analysis (storage). Even the same, TBARS varied along the experimental period. TBARS values ranged between 0.013mg MDA/kg of sample and 0.065mg MDA/kg of the sample, respectively at 15, and 60 days of storage. These data display the similarity between the action of the natural antioxidant derived from the balloon pepper, and the synthetic sodium erythorbate. In this study, all samples for maturation process were individually vacuum-packed and, possibly, this process was able to protect cholesterol and fatty acids, especially unsaturated ones, from adverse conditions that could have promoted oxidation, although it’s a relatively stable compound. [9] evaluated the efficacy of ascorbic acid on processing characteristics and lipid oxidation of pre-rigor salted chicken breasts during 7 days of vacuum-packaged storage, and suggest that pre-rigor salting with ascorbic acid could be effective in improving lipid oxidation stability during vacuum refrigerated storage, without negative impacts on processing characteristics. Smoked sausage samples also did not display significant differences (P>0.05) associated neither to the treatment nor the storage time. TBARS values ranged between 0.013 and 0.069mg MDA/kg of sample along the experimental period. This result may be associated with the degradation of MDA to other compounds due to the action of phenolic compounds produced during the smoking process. [10] used Adzuki bean at 0.2% in smoked and not smoked sausages. The authors described positive results in the control of lipid oxidation in both kinds of products and associated these results to the presence of polyphenols, which are rich in anthocyanins, in the extract of the Adzuki bean.
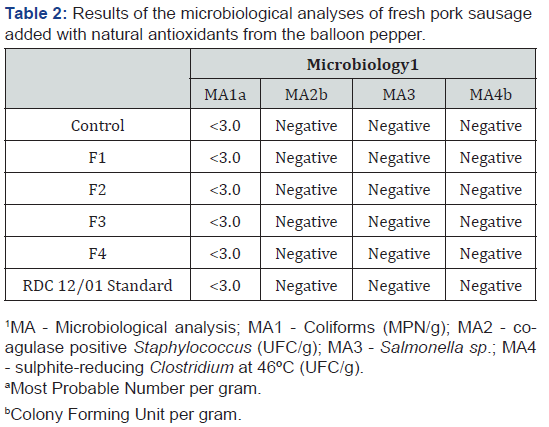
The storage process is directly associated with the development and survival of microorganisms. In order to provide quality to the products, it is crucial to preserve the microbiological stability. According to [11], the preservation of foods is due to the antimicrobial action addicted to the product, to the presence of lactic acid derived from the fermentation processes, and the control of pH. The enumeration of all the microorganisms searched was below the standard required by Brazilian laws [8]. In table 2, the excellent microbiological quality of the fresh sausage, as refers to coliforms (MPN/g), coagulase-positive Staphylococcus (UFC/g), Salmonella sp., and sulfate-reducing Clostridium at 46ºC (UFC/g). The high microbiological quality was due to the quality of the raw materials, in conjunction with good manufacturing practices along the production process, vacuum packaging of the product, and the use of additives, which prevented the growth of some species of microorganisms, beside the use of natural antioxidant, with its antimicrobial action.
Conclusion
We do not see the effects of formulas upon rancidification, once storage by freezing and vacuum packaging contributed positively to the
oxidation despite the use and type of antioxidant.
To know more about open access journal publishers click on https://juniperpublishers.com/



Comments
Post a Comment