The Exploration of Mycoviruses From Trichoderma Spp.- Juniper Publishers
Journal of Agriculture Research- Juniper Publishers
Mycoviruses are a kind of widespread virus, which can infect filamentous fungi and yeasts [1-3]. Most viruses can infect the host without obvious infection symptoms [1-2]. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) genomes always the main nucleotide style of mycoviruses, which has been a marker of the existence of viruses [4]. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses has divided all known branching viruses into 16 families and one unclassified group according to the mode of replication and genomics types of viruses [5]. At present, nine mycoviruses infecting Trichoderma spp. have been described [6-14]. 2009, Jom-in and Akarapisan provided the first description of two mycoviruses with sizes of 0.7kb and 1.1KB isolated from T. spp. [6]. Later, Yun et al. proposed that Lentinus edodes mycoviruses were widespread in Korea, and 32 different dsRNA-containing viruses were isolated from 315 strains of T. spp. [7]. Then, Lee et al. isolated an unclassified endovirus from Trichoderma atroviride, named Trichoderma atroviride mycovirus 1 (TaMV1) [8]. In 2018, Chun et al. obtained the complete genome sequences of two Trichoderma endoviruses, namely Trichoderma atroviride partitivirus 1 (TaPV1) and Trichoderma harzianum partitivirus 1(ThPV1) [9,10]. Meanwhile, a new mycovirus named Trichoderma asperellum dsRNA virus 1 (TaRV1) was reported in the laboratory of Guizhou Medical University in 2019 [11]. In 2019, Liu et al. isolated two unclassified dsRNA endoviruses, Trichoderma harzianum mycovirus 1 (ThMBV1) and Trichoderma harzianum mycovirus 1 (ThMV1), from 155 Trichoderma strains which were collected from the soils of Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia, China [12,13]. In 2019, You et al. from Huazhong Agricultural University isolated a new mycovirus from Trichoderma harzianum, named Trichoderma harzianum hypovirus 1 (ThHV1), which may be a member of Betahyprovirus [14]. In this paper, we chose 120 strains of T. spp. isolated from Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, and Heilongjiang of China, to screen mycoviruses using molecular biology methods, and three mycoviruses strains were recovered.
Materials and methods
Fungal strains
One hundred and twenty T. spp. strains were isolated from the forests and grasslands of Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia and Heilongjiang of China, in 2017–2018. The species of all of these strains were identified by the lab experiment, the information about these strains were in the supplemental table S1. All fungal strains were cultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates for 7 days at 28°C for the preparation of the next step.
Extraction of dsRNA
All fungal strains were transferred to in the potato dextrose liquid medium (PD), and placed on the shaker at 200 r/min and cultured at 28℃, after 2 days, collecting the mycelium for dsRNA extraction. DsRNA was extracted and purified from the mycelia by using CF-11 cellulose column chromatography [15]. Then, the samples were digested by RNase free DNase I (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) and S1 Nuclease (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions to remove any DNA and ssRNA contamination [13]. At last, electrophoresises of the samples were run in 1% agarose gel, and the dsRNA was detected by ultraviolet transillumination.
Results
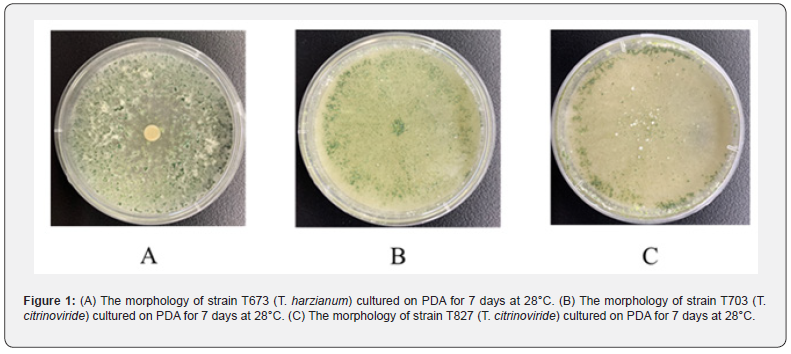
After 2 days’ culture in PD, the mycelium of 120 strains of T. spp. were collected, then dsRNA of the 120 strains were extracted by the molecular biology methods. Though the existing of dsRNA in the electrophoresis, the three Trichoderma strains with mycoviruses have been screened out. T673 was T. harzianum, T703 and T827 were T. citrinoviride, all of which were from Xinjiang province (Figures 1A, B, C). After dsRNA was extracted from mycelium, two fragments of 1.5 and 1.7 KB were found in strain T673 (T. harzianum), then DNase I and S1 nuclease were used to confirm the type of nucleic acid, and dsRNAs were identified (Figure 2A). In the strain of T703 (T. citrinoviride), only one fragment of 9 KB was found, and the dsRNA was digested by DNase I and S1 nuclease to confirm the properties of nucleic acid (Figure 2 B). With the same method, one dsRNA fragment of 9 KB was found in strain T827 (T. citrinoviride) (Figure 2C).

Discussion
In this paper, we obtained three strains of mycoviruses from 144 strains of T. spp. isolated from the soil, which can preliminarily prove that mycovirus existed in T. spp., and provided insight into how to locate and isolate mycoviruses from T. spp.. In the obvious researches, five genome sequences of mycoviruses from T. spp. were obtained, from which three strains were from T. harzianum [6-14]. In this issue, one mycovirus strain T-673 weas explored from T. harzianum, another two strains from T. citrinoviride. At present, for the investigation on DNA mycovirus was few in the nature, the DNA mycovirus from T. spp. has not been recovered [3]. All in all, the investigated dsRNA and DNA mycoviruses from T. spp. were few until now, which need to be explored more and more. In the future, nucleic acid type, the elimination, complete genome sequence, transmission mode and antagonistic effect on Trichoderma and biocontrol function of the mycovirus, as well as the interaction between fungi and mycoviruses, need to be revealed.
To know more about open access journal publishers click on Juniper publishers



Comments
Post a Comment