Efficiency of Entomopathogenic Fungi to Sugarcane White Leafhopper, Matsumuratettix hiroglyphicus (Matsumura) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae)- Juniper Publishers
Journal of Agriculture Research- Juniper Publishers
Sugarcane White Leafhopper, Matsumuratettix hiroglyphicus (Matsumura) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) is an economic important insect pest of sugarcane in Thailand. It represents as the reservoir of phytoplasma that cause sugarcane white leaf disease [1]. In recently, sugarcane white leaf disease spread out from the Northeastern region to the lower north region and the central region of Thailand. These causes sharply decrease in sugarcane yields. So that, entomopathogenic fungi become the discriminatory technique to control M. hiroglyphicus. This paper aims to evaluate the efficiency of three species of entomopathogenic fungi to M. hiroglyphicus adults in the laboratory.
Material and Methods
Insect culture
The adults of M. hiroglyphicus were collect lively by setting the light trap in sugarcane field that having the white leaf disease at Bueng Samakkhi district, Kamphaeng Phet province. Then, transferred them to the National Biological Control Research Center, Central Regional Center, Kasetsart University, Kamphaeng Saen campus, Nakhon Pathom' s laboratory for rearing. They were reared on the one month sugarcane that placed in the rounded plastic cages until we prompted to do the experiment and bioassay.
Study on pathogenicity of three species of entomo-pathogenic fungi to M. hiroglyphicus adults
The experiment consisted of three species of entomopathogenic fungi that were Metarhizium anisopliae isolated from the sugarcane longhorn beetle, Beauvaria brassiana isolated from the brown plant hopper and Purpureocillium lilacium (Paecilomyces lilacinus) isolated from M. hiroglyphicus compared with control, distill water mixed with 0.05% Triton X 100. Each treatment consisted of five replications that were five adults per one Petri-dish. The trial done by dropping 1µl of 108 conidia/ml of each fungus on each adult. They were placed in 25±2 °C and 70±2% RH. The data were checked for ten days, the adults were checked that the spores of each fungus grow cover their bodies by the necked eyes. The data were collected and calculated by statistic tool.
Bioassay of M. anisopliae to M. hiroglyphicus adults
Metarhizium anisopliae was the better candidate of entomopathogenic fungus for controlling M. hiroglyphicus adults. We used five concentrations of M. anisopliae; 105, 106; 107; 108 and 109 conidia/ml compared with distill water mixed with 0.05% Triton X 100. Each treatment consisted of five replications that were five adults per one Petri-dish. The trial done by dropping 1µl of each concentration of each fungus on individual adult. They were placed in 25±2 °C and 70±2% RH. The data were checked for ten days, the adults were checked that the spores of each fungus grow cover their bodies by the necked eyes. The data were collected and calculated LC50 by probit analysis.
Results and Discussion
Pathogenicity of three species of entomopathogenic fungi to M. hiroglyphicus adults
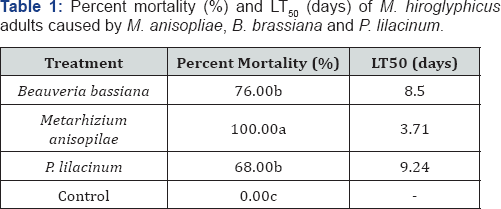
Percent mortality within a column followed by the same letter are not significantly different based on DMRT (P ≤0.05).
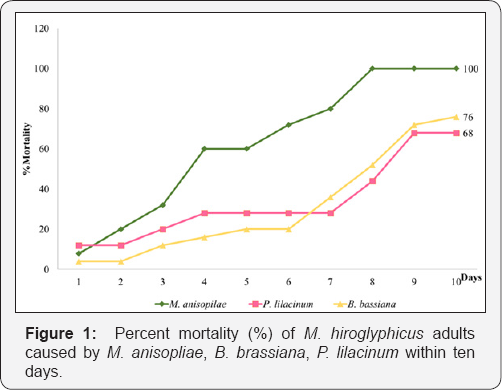
The results of pathogenicity of the three fungi revealed that they can infect M. hiroglyphicus adults. Percent mortalities of M. hiroglyphicus adults were significantly different between the three fungi there were 100, 76, 68 and 0 percent by M. anisopliae, B. brassiana, P. lilacinum and control, respectively. The LT50 indicated that M. anisopliae showed the rapid mortality was 3.71 days followed by B. brassiana, P. lilacinum that were 8.50 and 9.24 days, respectively (Table 1) and (Figure 1). Vestergaard et al. [2] treated M. anisopliae to adult Frankliniella occidentalis with resulted in at least 94% mortality at 7 days postinoculation. Annamalai et al. (2016) reported that B. brassiana showed percent mortality of 78.48% for the concentrations of 1.23x108spores/mL to Thrips tabaci. Jone et al. [3] reported that M. anisopliae strains were more virulent, with lower LT50 values, than were the B. bassiana strains [4].
Bioassay of M. anisopliae to M. hiroglyphicus adults
The result from pathogenicity indicated that M. anisopliae showed the highest percent mortality and lowest LT50 so that, we chosen M. anisopliae to do the bioassay to M. hiroglyphicus adults. The bioassay consisted of five treatments compared with control. The treatments were conidial suspensions 1x105, 1x106, 1x107, 1x108, 1x109conidia/ml and control. The results revealed that M. anisopliae showed 7.39x106 of the LT50 (Table 2). The probit analysis showed that R2 was 0.9638 (Figure 2).
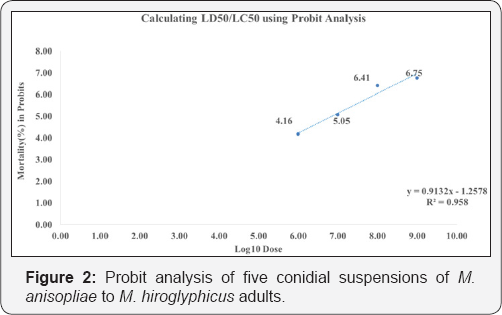
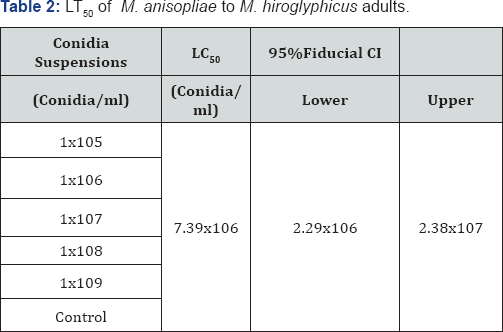
According to the results revealed that M. anisopliae isolated from D. buqueti showed the best pathocinity to M. hiroglyphicus adults with LT50 7.39x106. This fungus will be a promising biological control agent to control M. hiroglyphicus in sugarcane plantations.
To know more about open access journal publishers click on Juniper publishers



Comments
Post a Comment